 |
Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time. Then you can recall specific versions later. For the examples in this blog, you will use my source code on GitHub as the files being version controlled.
There are three types of Version Control Systems.
1. Local Version Control System (maintains track of files within the local system)
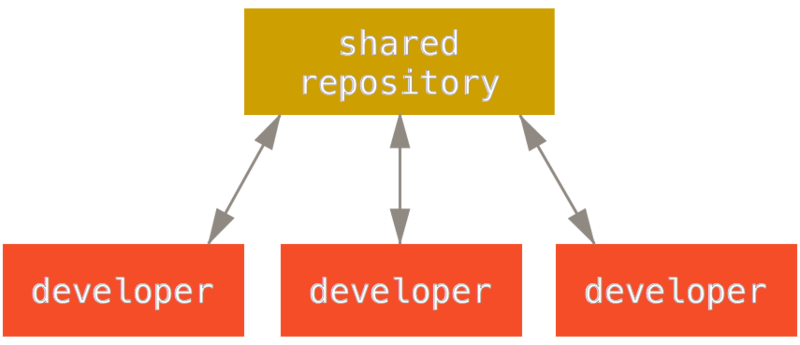
2. Centralized Version Control System ( files are tracked under the centralized server)
3. Distributed Version Control System (clients completely clone the repository including its full history)
Those version control systems are broken down into two main categories, centralized and decentralized (distributed).
The GIT terminology
Most version control systems involve the following concepts.
- Git: https://git-scm.com/
- Mercurial: https://www.mercurial-scm.org/
- Repository: The database.
- Changelog: A list of changes made.
- Syncing: Synchronizing your files with the latest from the repository.
- Reverting: Reloading the latest version from the repository.
- Server: The computer storing the repository.
- Client: The computer connecting to the repository.
- Merging: Applying the changes from one file to another.
- Conflict: Contradictions of files with each other.
- Resolving: Fixing the changes that contradict each other.
- Working Copy: Your local directory of files.
- Main: The primary location for code in the repository.
- Add: Creating a file into the repository for the first time.
- Revision: The version of a file.
- Head: The latest revision.
- Check out: Downloading a file from the repository.
- Check in: Uploading a file to the repository.
- Checkin Message: A short message.
- Branch: Creating a separate copy of a file/folder for private use.
- Locking: Taking control of a file so nobody else can edit it until you unlock it.
- Check out for edit: Checking out an “editable” version of a file
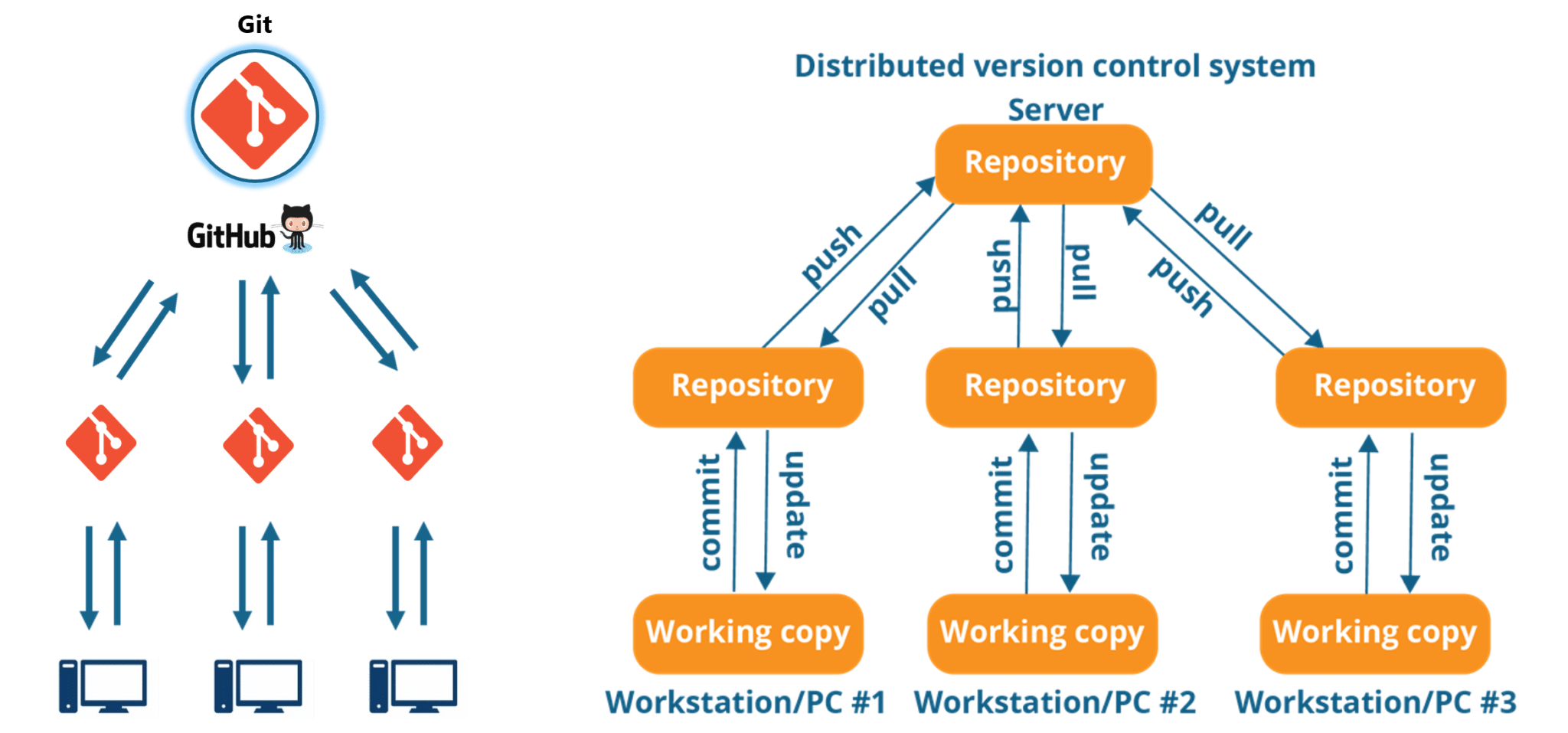
GIT as a distributed version control system
The official Git-Cheat-sheet can be downloaded from here.
|
 |
| Github.com |
Version Control Systems are sometimes known as Source Code Management systems(SCM) tools or Revision Control System (RCS). Git is one of the most popular VCS tools in use today. Git is a Distributed Version Control System and it is free and opensource.
Git is a distributed version-control system for tracking changes in source code during software development. It is designed for coordinating work among programmers, but it can be used to track changes in any set of files. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear work-flows. [Wikipedia]
Github Flow
The GitHub Flow is a light weight, branch based work-flow that is great for teams and projects with regular deployments. You can find more information on Github flow at lab.github.com
 |
| GitHub Flow |

Markdown is a way to style text on the web. You control the display of the document: formatting words as bold or italic, adding images, and creating list are just a few of the things we can do with Markdown. Mostly, Markdown is just regular text with a few non-alphabetic characters thrown in, like # or *.
GitHub uses its own version of markdown syntaxes that provides an additional set of useful features, many of which make it easier to work with content on GitHub.
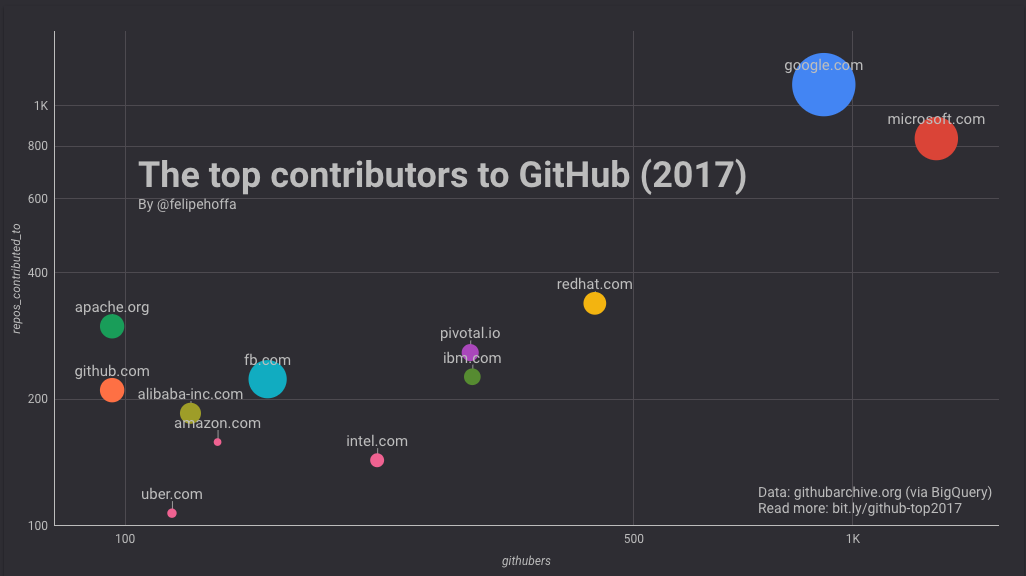
Contributing on GitHub
Contributing on GitHub is free. More than one million users have posted their own repositories on GitHub. But each of those repositories will not make sense and here you can see the top contributors on GitHub in 2017.
 So try out git and GitHub when you code! Start collaborating with millions of developers today!
So try out git and GitHub when you code! Start collaborating with millions of developers today!Mention any question bellow, we will answer it as soon as possible. Wait... something to remember... In case of fire? Here is the solution...
Commit it, Push it, Escape !
Happy Coding !
Comments